 The ketogenic diet, or the keto diet for short, is a low-carb, high-fat diet that has gained immense popularity in the past few years. The main aim of this diet is to induce a state of ketosis in the body, where it primarily burns fat for fuel instead of glucose.
The ketogenic diet, or the keto diet for short, is a low-carb, high-fat diet that has gained immense popularity in the past few years. The main aim of this diet is to induce a state of ketosis in the body, where it primarily burns fat for fuel instead of glucose.
Understanding Ketosis
Ketosis occurs when the body's carbohydrate intake is significantly reduced, and the liver starts producing ketones. These ketones serve as an alternative energy source for the body and are produced from stored fat. This metabolic state has been associated with numerous health benefits, including weight loss, improved mental clarity, and increased energy levels.
The Mechanism of Keto
On a standard diet, the body relies heavily on glucose, which is derived from carbohydrates, as its primary source of energy. However, on a keto diet, carbohydrate intake is restricted to a bare minimum, forcing the body to switch its fuel source to fat. This switch triggers the production of ketones, which are used to power the body's functions.
Benefits of the Keto Diet
Weight Loss: The keto diet is widely known for its effectiveness in promoting weight loss. By restricting carbohydrates and increasing fat consumption, the body is driven into ketosis, leading to enhanced fat burning. Improved Mental Focus: Many keto enthusiasts report experiencing increased mental clarity and improved focus when following this diet. This could be attributed to the stable energy levels provided by ketones. Steady Energy Levels: Unlike the fluctuations associated with glucose metabolism, a ketogenic diet provides steady energy levels throughout the day. This is particularly beneficial for athletes and individuals with demanding lifestyles. Reduced Inflammation: Some studies suggest that the keto diet may help reduce inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is linked to various health issues, including heart disease and certain types of cancer.
Foods to Eat on a Keto Diet
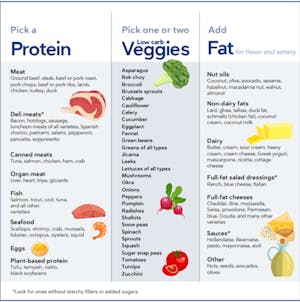
When it comes to the keto diet, it is essential to consume foods that are low in carbohydrates and high in healthy fats. Here are some examples of foods that are commonly consumed on a keto diet: Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines) Meat and poultry (grass-fed beef, chicken, turkey) Eggs Avocados Nuts and seeds Low-carb vegetables (leafy greens, cauliflower, broccoli) Healthy oils (olive oil, coconut oil, avocado oil)
Foods to Avoid on a Keto Diet
To maintain a state of ketosis, it is crucial to avoid foods that are high in carbohydrates. Here are some foods that should be restricted or completely eliminated while following a keto diet: Grains and starches (bread, pasta, rice) Sugary foods and beverages Fruits (high in natural sugars) Legumes (beans, lentils) Processed and packaged snacks Sweetened dairy products (yogurt, flavored milk)
Potential Side Effects
While the keto diet can be highly effective for weight loss and improving overall health, some individuals may experience initial side effects, commonly known as the "keto flu." These side effects can include fatigue, headaches, dizziness, and digestive issues. However, they are usually temporary and will subside as the body adapts to the new metabolic state.
Is the Keto Diet Right for You?
The keto diet can be a great option for individuals looking to lose weight, improve their energy levels, and enhance mental focus. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new diet, especially if you have any underlying medical conditions or are taking medication. Conclusion: The ketogenic diet, with its focus on low carbohydrates and high healthy fats, has been shown to provide various benefits, including weight loss, improved mental clarity, and increased energy levels. By understanding the basics of ketosis and following a proper meal plan, individuals can embark on a successful keto journey and achieve their desired health and wellness goals.