 B vitamins are crucial for maintaining a healthy body and mind. They play an essential role in converting food into energy, ensuring proper brain function, supporting cell metabolism, and maintaining a healthy nervous system. Among the various B vitamins, folate (also known as vitamin B9) holds significant importance. However, the benefits extend beyond folate alone. Let's dive deeper into the world of B vitamins and discover their diverse functions.
B vitamins are crucial for maintaining a healthy body and mind. They play an essential role in converting food into energy, ensuring proper brain function, supporting cell metabolism, and maintaining a healthy nervous system. Among the various B vitamins, folate (also known as vitamin B9) holds significant importance. However, the benefits extend beyond folate alone. Let's dive deeper into the world of B vitamins and discover their diverse functions.
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) – Energy Production and Nervous System Support
Vitamin B1, also known as thiamine, is responsible for converting carbohydrates into energy, making it a key player in energy production. Thiamine also plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy nervous system by supporting nerve function and signal transmission. It is found abundantly in whole grains, legumes, and nuts.
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) – Antioxidant Powerhouse and Energy Booster
Vitamin B2, or riboflavin, acts as a potent antioxidant, protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals. Additionally, it plays a vital role in energy production by aiding in the breakdown of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Riboflavin-rich sources include dairy products, green leafy vegetables, and fortified cereals.
Vitamin B3 (Niacin) – Metabolism and Cardiovascular Health
Vitamin B3, also known as niacin, is essential for metabolic processes in the body, aiding in the conversion of food into energy. It also contributes to cardiovascular health by promoting healthy cholesterol levels. Niacin is present in foods like poultry, fish, peanuts, and whole grains.
Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) – Stress Buster and Skin Health
Pantothenic acid, or vitamin B5, is often referred to as a stress buster due to its crucial role in the production of stress-related hormones. It also supports healthy skin by promoting the growth and maintenance of skin cells. Excellent sources of vitamin B5 include meat, eggs, whole grains, and avocados.
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) – Brain Development and Mood Regulation
Vitamin B6, also known as pyridoxine, plays a vital role in brain development and function. It is involved in the synthesis of key neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, helping regulate mood and behavior. Foods like fish, poultry, bananas, and spinach are high in vitamin B6.
Vitamin B9 (Folate) – Cell Growth and DNA Formation
Folate, or vitamin B9, is essential for various bodily processes, including DNA formation, red blood cell production, and overall growth and development. Adequate folate intake is especially crucial during pregnancy, as it helps prevent neural tube defects in the developing fetus. Dark leafy greens, citrus fruits, legumes, and fortified grains are excellent dietary sources of folate.
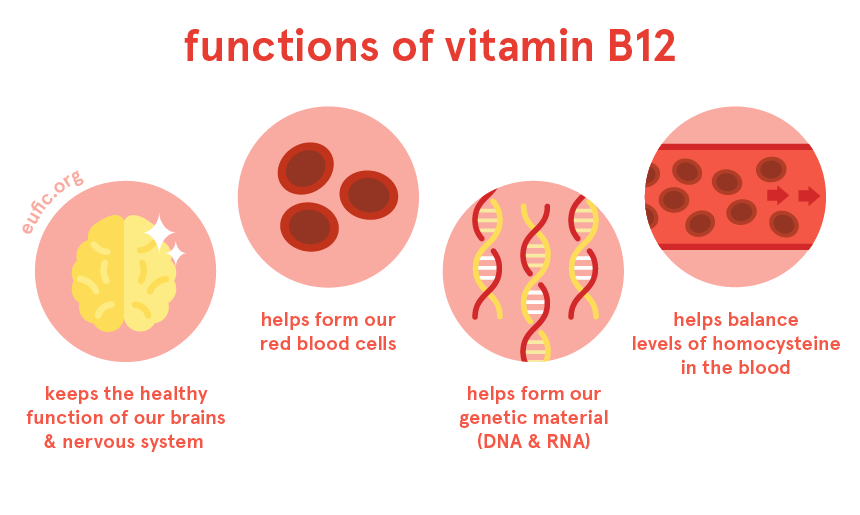
Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) – Nerve Health and Energy Production
Vitamin B12, or cobalamin, is crucial for nerve health as it plays a significant role in the formation of myelin, the protective layer surrounding nerves. It also aids in the production of red blood cells and DNA. Animal-based foods such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products are the primary sources of vitamin B12.
Conclusion
The B vitamin family, including folate and other crucial members, offers numerous benefits to our bodies. From energy production and nervous system support to brain development and cardiovascular health, each B vitamin plays a unique role. Ensuring an adequate intake of these vitamins through a balanced and varied diet is essential for maintaining optimal health. So, make sure to include an array of B vitamin-rich foods in your meals to enjoy their incredible benefits.